How Do GLP-1s Work? Benefits for Weight Loss & Diabetes
In recent years, GLP-1s have become a hot topic in both medical and wellness circles. Whether you’re managing type 2 diabetes or struggling with weight loss, you may have heard of medications like Ozempic, Wegovy, or Mounjaro. But what exactly are GLP-1s? How do they work inside your body? And why are they being hailed as game-changers in modern health?
Let’s break it all down in simple, no-jargon English so you can make informed decisions—because your health deserves clarity, not confusion.
What Are GLP-1s?
Full Form and Meaning of GLP-1
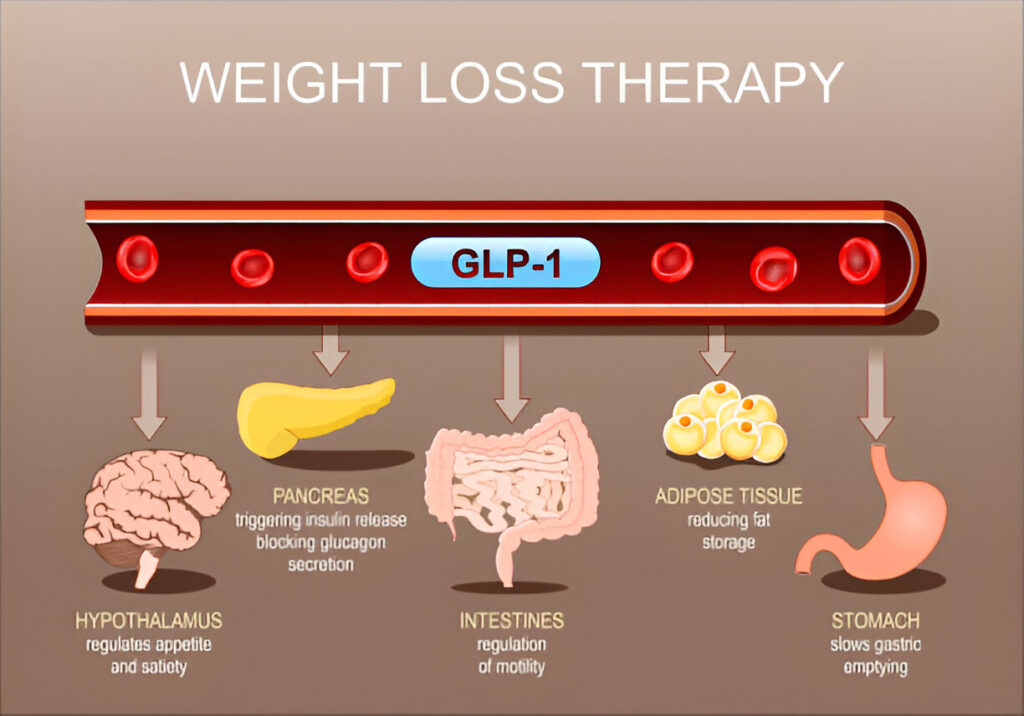
GLP-1 stands for Glucagon-Like Peptide-1. It’s a hormone that your body naturally produces in your gut after you eat. Think of it as a helper that tells your body, “Hey, food just came in—let’s manage it smartly.”
Natural Role of GLP-1 in the Body
GLP-1 has several important jobs:
- It helps your pancreas release insulin (the hormone that lowers blood sugar).
- It slows down how quickly food leaves your stomach.
- It sends signals to your brain to say, “I’m full now.”
In short, GLP-1 is part of the body’s natural appetite and sugar control system.
Why GLP-1s Became Important in Medicine
Scientists realized that some people don’t make enough GLP-1 or their bodies don’t respond to it properly. This can lead to issues like:
- High blood sugar
- Insulin resistance
- Constant hunger or cravings
So, researchers developed GLP-1 receptor agonists—lab-made drugs that mimic the natural hormone and help your body regulate itself better.
How Do GLP-1s Work in the Human Body?
Understanding how GLP-1s function helps explain why they’re so effective for weight loss and blood sugar control.
Boosting Insulin Production
When you eat, GLP-1 tells your pancreas to release insulin—but only if your blood sugar is high. This is different from insulin injections, which work no matter what. GLP-1s are smarter—they act when needed.
Slowing Down Stomach Emptying
GLP-1 drugs delay how quickly food leaves your stomach. The benefit? You stay full longer, eat less, and avoid sugar spikes.
Reducing Appetite and Cravings
These medications directly impact the brain’s appetite centers. You feel full faster and crave food less. This is a big reason why GLP-1s are popular for weight loss.
Supporting Blood Sugar Regulation
GLP-1s help the liver reduce the amount of glucose it releases and prevent blood sugar crashes. This creates a smoother, more stable energy curve throughout your day.
GLP-1s for Diabetes: How They Help
If you or someone you love has type 2 diabetes, GLP-1s might offer relief and control without the risks of older medications.
Better Blood Sugar Control
Studies show that GLP-1 drugs can lower A1C levels (a long-term marker of blood sugar) by up to 1.5%—a significant number for diabetics.
Lower Risk of Hypoglycemia
Unlike insulin, GLP-1s only activate when your blood sugar is high. This reduces the risk of dangerously low sugar levels (hypoglycemia).
Fewer Complications Over Time
Long-term use may protect against diabetes-related complications like:
- Kidney damage
- Heart disease
- Nerve pain
Many patients see improved overall health beyond just glucose control.
GLP-1s for Weight Loss: Why They’re So Popular
Even people without diabetes are now turning to GLP-1s. Why? Because they’re losing 15% to 20% of their body weight—without intense diets or workouts.
How They Help You Eat Less
Because GLP-1s delay stomach emptying and curb appetite, users feel full with less food and fewer calories. Over time, this leads to consistent weight loss.
Effect on Metabolism and Fat Storage
GLP-1s can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and encourage your body to burn more fat instead of storing it.
What Research Says About Weight Loss Results
In a 68-week clinical trial of Wegovy, participants lost an average of 15% of their body weight compared to just 2% in the placebo group. That’s not just a little drop—it’s life-changing.
Common GLP-1 Drugs in the Market
Here are the top names you’ll come across:
Ozempic
Used mainly for type 2 diabetes but widely known for weight loss benefits. Weekly injection.
Wegovy
FDA-approved specifically for chronic weight management. Same active ingredient as Ozempic but higher dose.
Mounjaro
Newest to the scene. Targets GLP-1 and GIP receptors, showing even greater weight loss than Ozempic in some studies.
Rybelsus and Others
Rybelsus is the first oral GLP-1 drug, offering an option for those who don’t want injections.
How Are GLP-1s Taken?
Injection vs Oral Tablets
- Injections: Weekly pens like Ozempic and Wegovy.
- Oral tablets: Rybelsus, taken once daily.
Dosage Frequency
Most injectables are taken once a week, while oral options are daily. Your doctor will start you at a low dose and gradually increase it to minimize side effects.
What to Expect During Treatment
Early weeks may include nausea, bloating, or constipation. These usually go away as your body adjusts. Appetite drops noticeably within 1–2 weeks.
Potential Side Effects of GLP-1s
Like any drug, GLP-1s aren’t perfect.
Most Common Side Effects
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Headache
These are usually mild and temporary.
Rare But Serious Risks
- Pancreatitis
- Gallbladder issues
- Kidney problems
Talk to your doctor about these risks, especially if you have a history of these conditions.
Who Should Avoid GLP-1s?
- People with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer
- Individuals with pancreatitis
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting.
Are GLP-1s Safe for Long-Term Use?
Clinical Trials and Safety Data
GLP-1s have been studied in large-scale trials for over a decade. Most show long-term benefits with manageable risks.
What Doctors Recommend
Doctors are increasingly prescribing GLP-1s for long-term weight and diabetes management—especially when lifestyle changes alone don’t work.
Ongoing Research
New studies are testing their impact on:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Cardiovascular protection
- Inflammatory conditions
These drugs might have more uses than we originally thought.
Who Can Benefit Most from GLP-1s?
People with Type 2 Diabetes
If you’re struggling with blood sugar control despite other medications, GLP-1s could be your missing link.
Individuals with Obesity
Those with a BMI over 30, or over 27 with health issues (like high blood pressure), may qualify for GLP-1 treatment for weight loss.
Those Struggling with Appetite Control
If your hunger feels constant and willpower isn’t enough, these drugs can provide physiological support—not just mental effort.
GLP-1s vs Other Diabetes and Weight Loss Drugs
How They Compare with Insulin
Insulin works fast but can cause weight gain and low blood sugar. GLP-1s do the opposite—help you lose weight and stabilize sugar naturally.
Comparison with Metformin and SGLT2 Inhibitors
- Metformin: Often a first-line diabetes drug, but less effective for weight loss.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: Help you pee out excess sugar—great for the heart but not as strong for weight loss.
GLP-1s often work better for both goals.
Cost and Accessibility
GLP-1s can be expensive—sometimes $1,000+ per month without insurance. But many insurance plans are starting to cover them, and patient assistance programs are available.
Final Thoughts: Should You Consider GLP-1s?
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
- Am I a good candidate?
- What are the risks for my health history?
- Will insurance cover it?
What Results Can You Expect?
Most people see results within 4–8 weeks:
- Lower blood sugar
- Reduced hunger
- Steady weight loss of 1–2 pounds per week
Making a Safe and Informed Decision
GLP-1s aren’t magic—but they’re science-backed, proven tools for better health. Combine them with smart eating and movement, and they can help you rewrite your health story.

